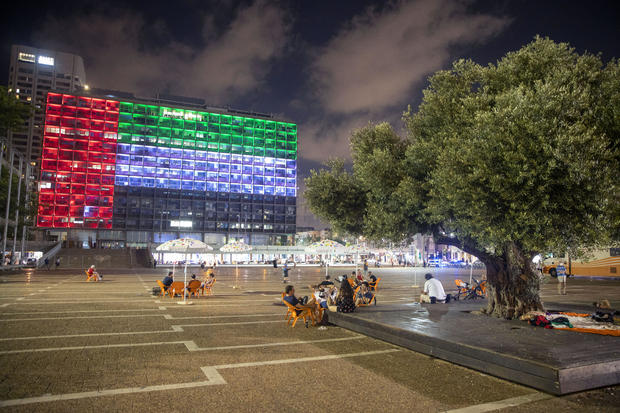
UAE formally ends Israel boycott amid U.S.-brokered deal to normalize relations
The ruler of the United Arab Emirates issued a decree Saturday formally ending the country's boycott of Israel amid a U.S.-brokered deal to normalize relations between the two countries. The announcement allows trade and commerce between the UAE – home to Abu Dhabi and Dubai – and Israel, home to a thriving diamond trade, pharmaceutical companies and tech start-ups.
The announcement further cements the August 13 deal opening up relations between the two nations, which required Israel to halt its contentious plan to annex occupied West Bank land sought by the Palestinians.
The state-run WAM news agency said the decree formally ending the boycott came on the orders of Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed Al Nahyan, the ruler of Abu Dhabi and the Emirates' leader.
WAM said the new decree allows Israelis and Israeli firms to do business in the UAE, a federation of seven sheikhdoms on the Arabian Peninsula. It also allows for the purchase and trade of Israeli goods.
"The decree of the new law comes within the UAE's efforts to expand diplomatic and commercial cooperation with Israel," WAM said. It lays out "a roadmap toward launching joint cooperation, leading to bilateral relations by stimulating economic growth and promoting technological innovation."
Already, some Israeli firms had signed deals with Emirati counterparts. But the repeal of the law widens the likelihood of other joint ventures, such as in aviation or in banking and finance.
Dubai International Airport has been the world's busiest for international travel for years. The Dubai International Financial Center also hosts major firms who trade in the hours between Asian and European markets. Dubai already has a major gold market and growing diamond trade.
Emirati firms likely also want to access Israeli technological know-how. Some already had even before the deal – with the cybersecurity firm DarkMatter reportedly hiring Israeli military-trained hackers.
On Monday, the first direct commercial flight by Israel's flagship carrier El Al is expected in Abu Dhabi, carrying U.S. and Israeli officials including President Donald Trump's son-in-law, Jared Kushner. Telephone calls already can be made between the nations.
The decree formally eliminates a 1972 law on the UAE's books since just after the country's formation. That law mirrored the widely held stance by Arab nations at that time that recognition of Israel would only come after the Palestinians had an independent state of their own.
The UAE is becoming the third Arab nation after Egypt and Jordan to currently have diplomatic relations with Israel. However, while widespread public distrust of Israel persists in those nations, the UAE never fought a war against Israel, nor did it have a historic Jewish population.