Poll: Do you have "fear of missing out"?
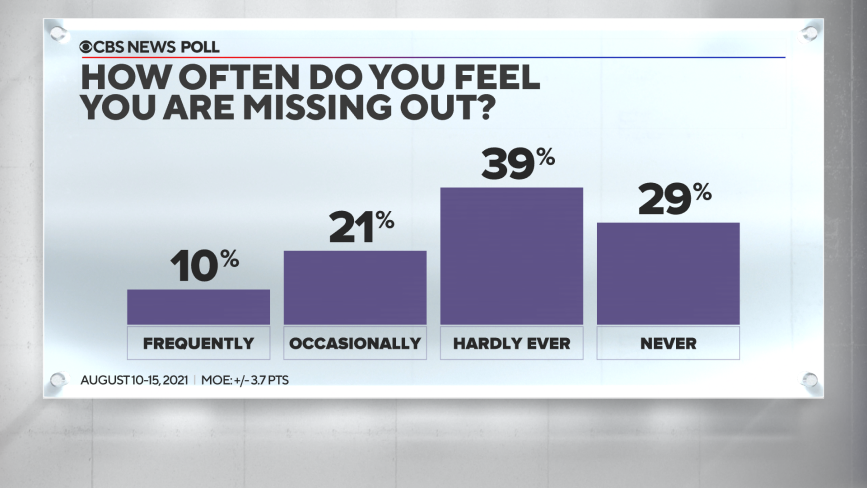
"The fear of missing out" — sometimes referred to as "FOMO" — is the worry that you might be missing out on activities that others are doing, and it seems many Americans feel this way at least some of the time. Thirty-one percent say they feel they are missing out on fun activities that others are doing at least occasionally, including 1 in 10 Americans who say they feel this way frequently.
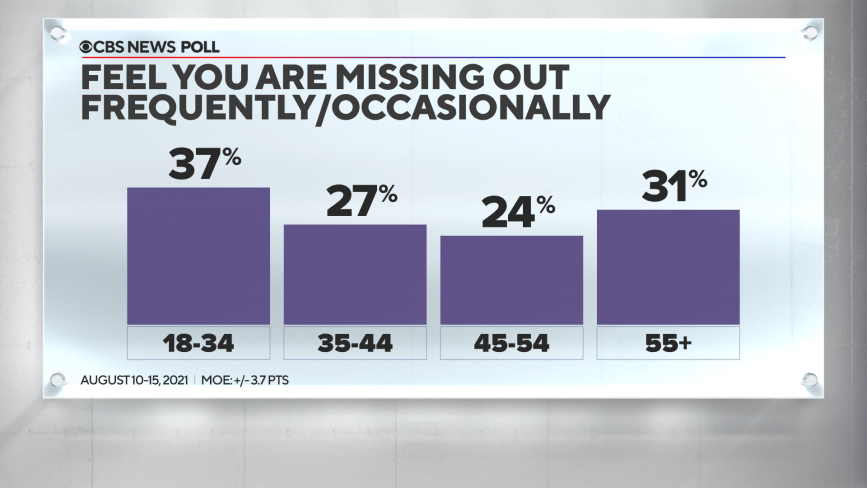
Among adults, the feeling they are missing out is felt most often by younger Americans: 37% of those under 35 feel this way at least occasionally. But many older Americans feel this way too. While the percentage who feel this way at least occasionally decreases among those between 35 and 54, it rises again among adults 55 and older.
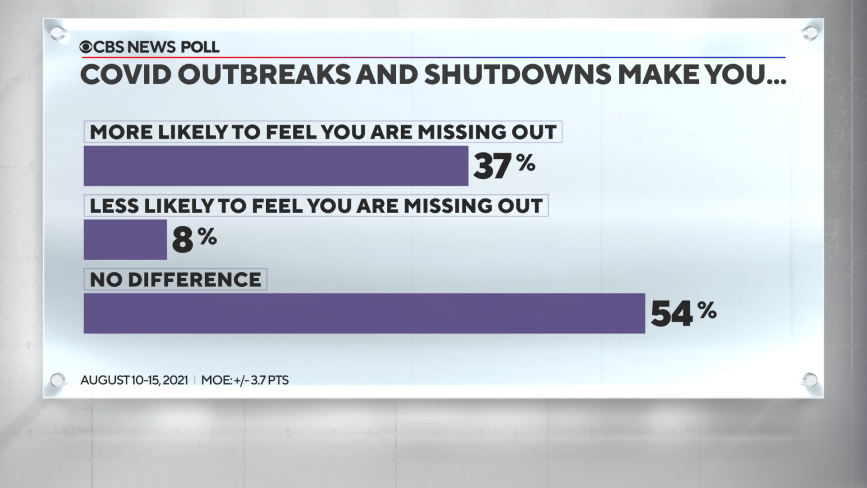
The coronavirus outbreak — as well as the subsequent economic shutdowns — seems to have exacerbated the feeling of missing out among even more Americans. Overall, 37% of Americans — and 46% of those who feel they are missing out frequently — say the coronavirus outbreak has made them more likely to feel they are missing out.
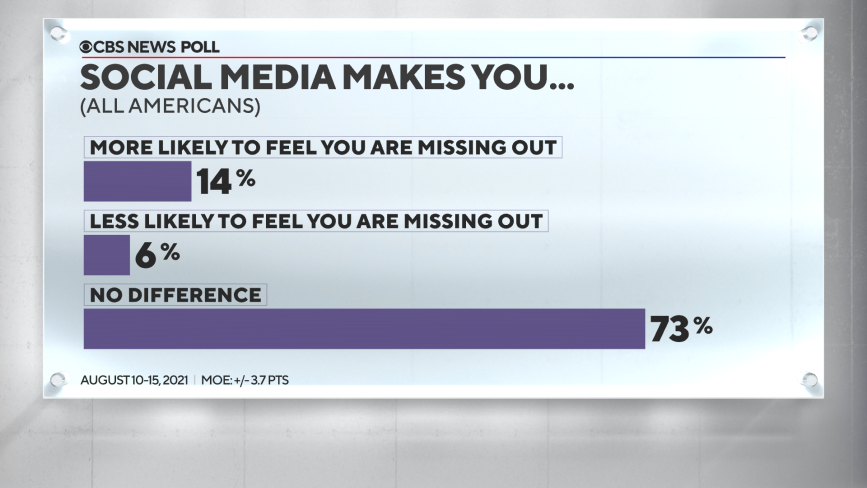
Some have tied social media sites to the feeling of missing out on things, and while most Americans don't think social media plays much of a factor, younger Americans are more likely to say they feel its effects. Over a quarter of Americans under 35 say social media makes them more likely to feel they are missing out.
This poll was conducted by telephone July 13-18, 2021 among a random sample of 1,006 adults nationwide. Data collection was conducted on behalf of CBS News by SSRS of Glen Mills, Pennsylvania. Phone numbers were dialed from samples of both standard land-line and cellphones.
The poll employed a random digit dial methodology. For the landline sample, a respondent was randomly selected from all adults in the household. For the cell sample, interviews were conducted with the person who answered the phone.
Interviews were conducted in English and Spanish using live interviewers. The data have been weighted to reflect U.S. Census figures on demographic variables. The error due to sampling for results based on the entire sample could be plus or minus 3.6 points. The error for subgroups may be higher and is available by request. The margin of error includes the effects of standard weighting procedures which enlarge sampling error slightly. This poll release conforms to the Standards of Disclosure of the National Council on Public Polls.