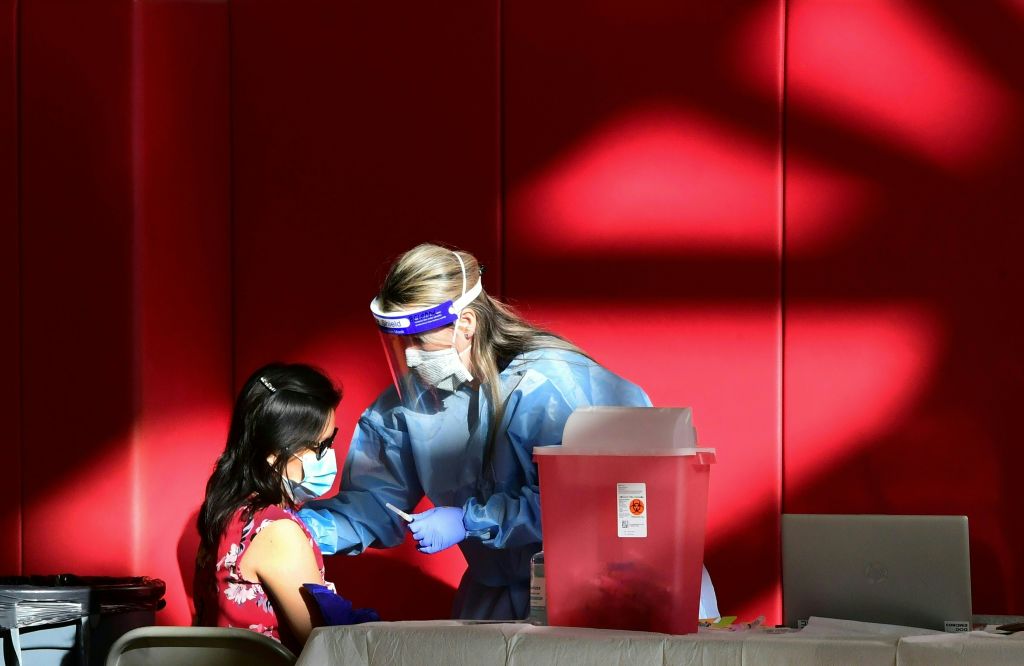
Johnson & Johnson starts trial of single-dose COVID-19 vaccine
Johnson & Johnson is starting a huge study to test if a single-dose COVID-19 vaccine can protect people against the coronavirus. The study, launching Wednesday, will be one of the world's largest coronavirus vaccine studies so far, involving 60,000 volunteers in the U.S., South Africa, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru.
A handful of other vaccines in the U.S. — including shots made by Moderna and Pfizer — as well as drug developers in other countries are already in final-stage testing. Hopes are high that answers about at least one candidate being tested in the U.S. could come by year's end, maybe sooner.
Pfizer and its partner BioNTech may be the first to learn if their vaccine works, with the companies planning to look at results after 32 coronavirus infections have occurred in their 44,000-person trial, according to Bloomberg News. That could occur as soon as September 27, analytics firm Airfinity told Bloomberg.
Recent U.S. data about COVID-19 "are unambiguously bad," Pantheon Economics chief economist Ian Shepherdson wrote in a Wednesday research note. "Over the past week, the number of daily new confirmed cases has risen by 14.5% compared to the previous week."
Meanwhile, U.S. health officials insist the race for a vaccine isn't cutting corners.
"We want to do everything we can without sacrificing safety or efficacy — we're not going to do that — to make sure that we end up with vaccines that are going to save lives," Dr. Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, told reporters.
But many vaccine specialists question whether the Food and Drug Administration will stick to that goal under intense pressure from the Trump administration. President Donald Trump has consistently presented a faster timeline for a new vaccine than experts say is adequate to fully test the candidates.
Testing of still another experimental vaccine, made by AstraZeneca, remains on hold in the U.S. as officials examine a safety question, even though studies have resumed in other countries.
Earlier this week, Vice President Mike Pence urged state governors to "do your part to build public confidence that it will be a safe and effective vaccine."
Dr. Anthony Fauci, the top U.S. infectious disease expert, added in the call to governors that he is confident in "a tried and true process" that has checks and balances built in, including an independent board evaluating the progress of each vaccine trial, as well as "the integrity of the FDA."
A recording of the call was provided to The Associated Press.
Senators were scheduled to question FDA Commissioner Stephen Hahn, Fauci and other administration officials later Wednesday about the pandemic response.
Even if the FDA were to allow emergency use of a vaccine by year's end, supplies would be limited and given first to vulnerable groups such as health workers. Most Americans aren't likely to receive a vaccine until sometime next year.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention wants states to get ready now to roll out vaccinations, which will present enormous logistical challenges. On Wednesday the CDC was set to announce distribution of $200 million in congressionally approved funds to help begin setting up operations.
Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar said the COVID-19 vaccine campaign will build on longstanding cooperation between the federal government and the states on immunizations.
J&J's vaccine is made with slightly different technology than others in late-stage testing, modeled on an Ebola vaccine the company created. Unlike the other three vaccines that started late-stage testing in the U.S., it requires only one shot, not two. Despite a later start to testing than some of its competitors, Dr. Paul Stoffels, J&J's chief scientific officer, told reporters that the study was large enough to yield answers possibly by early next year.