Webb telescope captures 'green monster' inside a young supernova
(CNN) -- The James Webb Space Telescope has spied colorful, never-before-seen details in one of the most well-observed remnants of an exploded star.
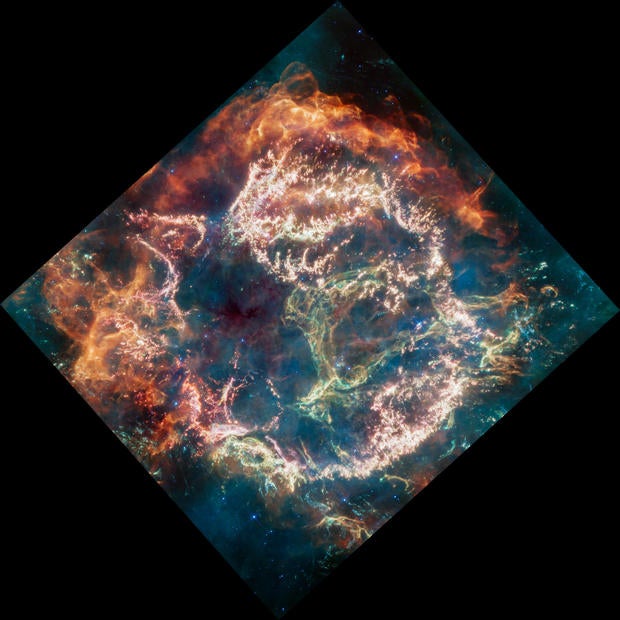
The glowing gas and dust of Cassiopeia A is all that remains of a star that exploded in a supernova, and its light reached Earth for the first time 340 years ago. It's the youngest known supernova remnant in our galaxy, which is why the celestial object has been studied by a multitude of ground and space-based telescopes.
Cassiopeia A is located 11,000 light-years away in the Cassiopeia constellation, and the remnant stretches for 10 light-years.
Insights from Cas A, as the remnant is also known, allow scientists to learn more about how stellar explosions occur.
Astronomers turned the Webb telescope and its instruments in the direction of Cas A to see if the observatory's infrared capabilities could pick up anything other telescopes have missed. Infrared light is invisible to the human eye, allowing Webb to spy otherwise invisible aspects of the universe.
"Cas A represents our best opportunity to look at the debris field of an exploded star and run a kind of stellar autopsy to understand what type of star was there beforehand and how that star exploded," said Danny Milisavljevic, assistant professor at Purdue University and principal investigator of the Webb program that captured the new observations, in a statement.
"Compared to previous infrared images, we see incredible detail that we haven't been able to access before," said co-investigator Tea Temim, research astronomer at Princeton University, in a statement.
Webb's new infrared image of Cas A has been translated into visible light so the human eye can see the remnant's colors. Red and orange light on the remnant's exterior indicates warm dust, where material ejected from the star before it exploded is colliding with surrounding gas and dust.
Inside the bubble-like structure of the remnant, bright pink light can be seen, along with features that resemble clumps and knots. This material came from the exploded star and includes glowing heavy elements like argon, neon and oxygen.
A bright green loop along the right side of the bubble has also captured the interest of researchers.
"We've nicknamed it the Green Monster in honor of Fenway Park in Boston. If you look closely, you'll notice that it's pockmarked with what look like mini-bubbles," said Milisavljevic. "The shape and complexity are unexpected and challenging to understand."
The team is still trying to understand the sources behind all of the different colors in the image.
Studying remnants like Cas A can help scientists understand cosmic dust, a building block for stars and planets, and how exploded stars release elements crucial for life.
"By understanding the process of exploding stars, we're reading our own origin story," Milisavljevic said. "I'm going to spend the rest of my career trying to understand what's in this data set."
The operations center for the telescope is in Baltimore City, at the Space Telescope Science Institute on the Johns Hopkins campus.
The-CNN-Wire
™ & © 2023 Cable News Network, Inc., a Warner Bros. Discovery Company. All rights reserved.