"Almost human" - Homo naledi
Scientists announced September 10, 2015 the discovery of a new member of the human family tree; an "almost human" being called Homo naledi.
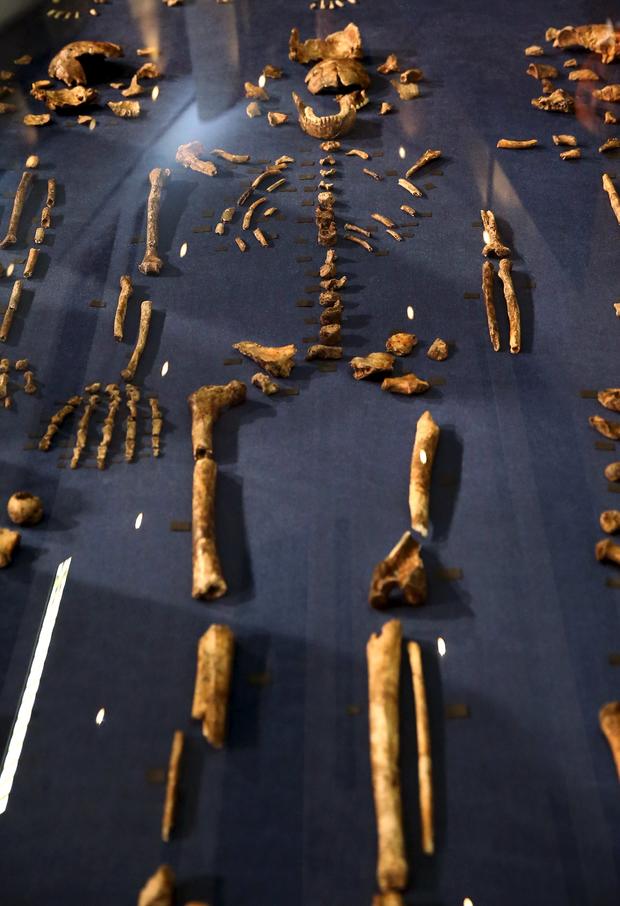
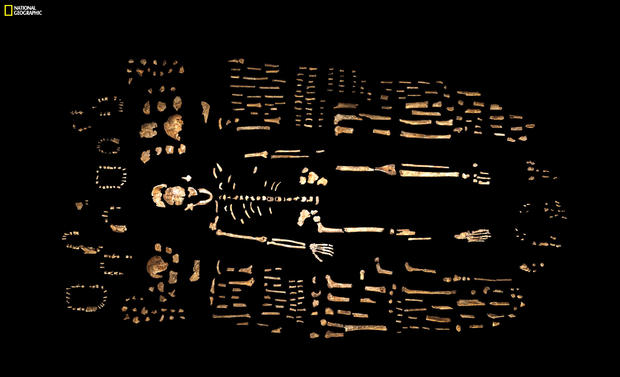
This photo, provided by National Geographic from their October 2015 issue, shows a composite skeleton of Homo naledi surrounded by some of the hundreds of other fossil elements recovered from the Rising Star cave in South Africa, pictured at the Evolutionary Studies Institute of the University of the Witwatersrand in Johannesburg.
Homo naledi
This photo taken March 2015 and provided by National Geographic from their October 2015 issue shows a reconstruction of Homo naledi's face by paleoartist John Gurche at his studio in Trumansburg, New York.
Homo naledi
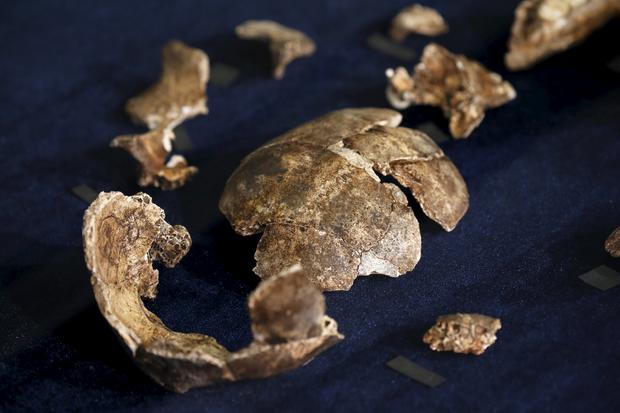
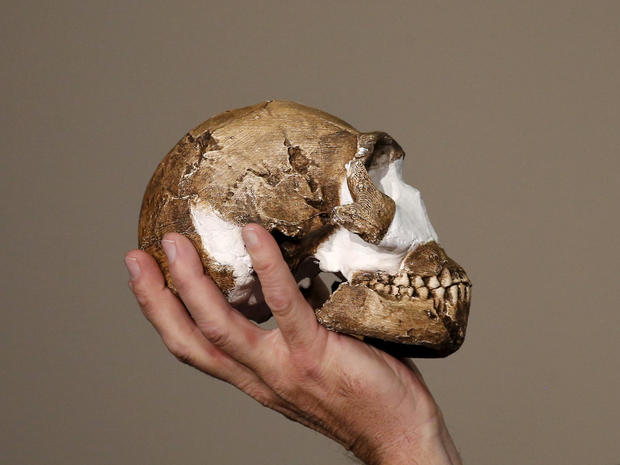
Professor Lee Berger, a renowned paleoanthropologist who led the expedition team, holds a replica of the skull of a newly discovered ancient species, named Homo naledi, during its unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10 2015.
Fossils of the creature were unearthed in a deep cave near the famed sites of Sterkfontein and Swartkrans, treasure troves 50 km (30 miles) northwest of Johannesburg that have yielded pieces of the puzzle of human evolution for decades. The area outside of Johannesburg is referred to as the "Cradle of Humankind."
Homo naledi
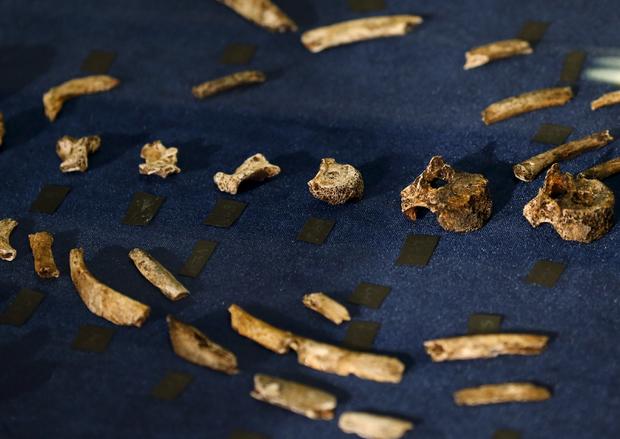
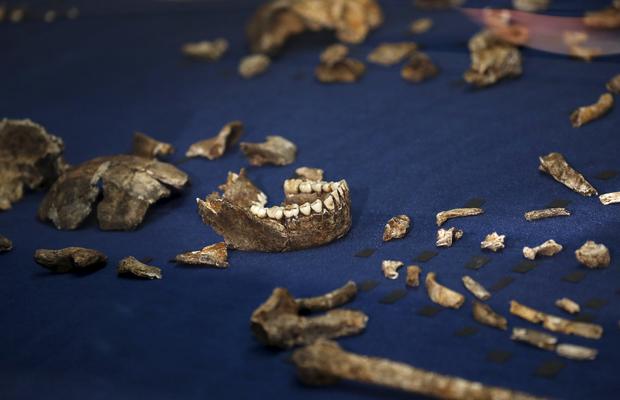
Fossils of a newly discovered ancient species Homo naledi are pictured during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Humanity's claim to uniqueness just suffered another setback: scientists reported on Thursday that the newly discovered ancient species related to humans also appeared to bury its dead.
Homo naledi
Fossils of a newly discovered ancient species, Homo naledi are pictured during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
The new species has been named Homo naledi: Homo indicating the creatures human evolution and naledi in honor of the Rising Star cave where it was found. Naledi means "star" in South Africa's Sesotho language.
Homo naledi
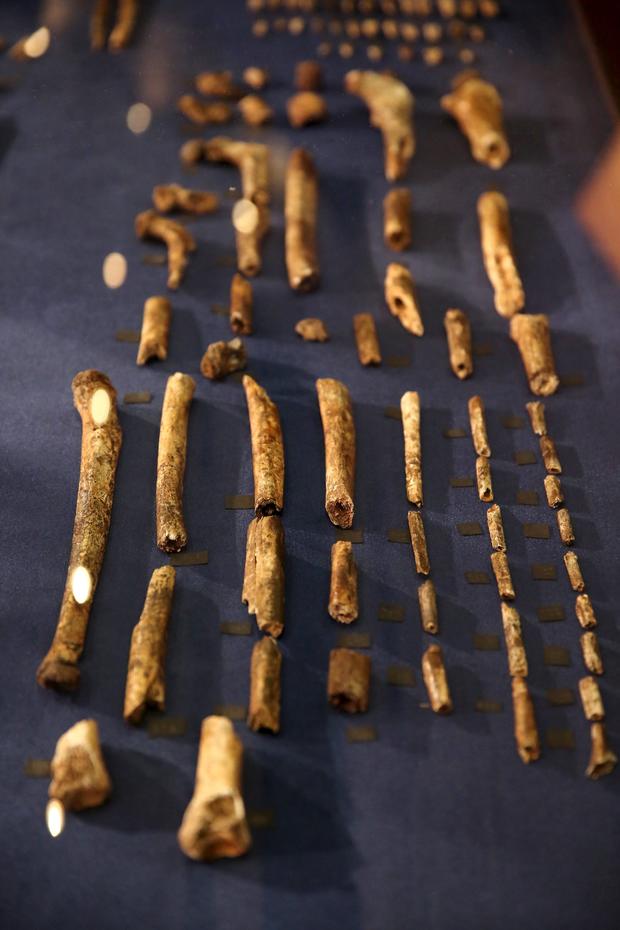
Hand bones of Homo naledi are pictured during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Homo naledi is estimated to be about 2.5 to 2.8 million years old.
Homo naledi
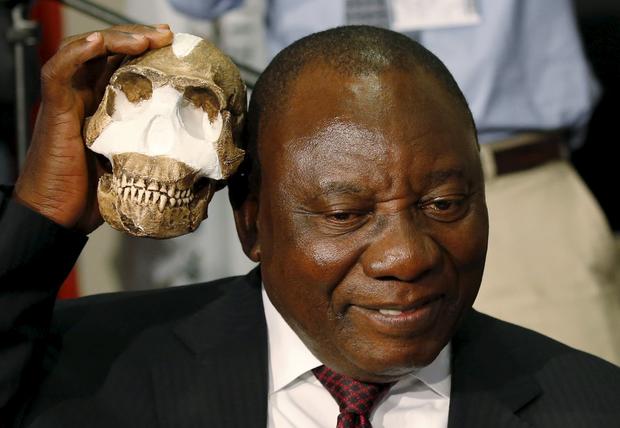
South Africa's Deputy President Cyril Ramaphosa holds a replica of the skull of a newly discovered ancient species, Homo naledi, during its unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10 2015.
At about 5 feet tall and only 100 or so pounds, and with a brain only about the size of an average orange, Homo naledi is a startling combination of australopith-like and human-like features that, until now, was entirely unknown to science, researchers said.
Homo naledi
South African Deputy President Cyril Ramaphos (C) and professor Lee Berger hold a replica of the skull of a Homo Naledi in Maropeng, near Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Berger describes the creature as a new species of human relative.
Homo naledi
Fossils of a Homo naledi are pictured during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Professor Berger claims Homo naledi is not human, but did practice something very human - disposing of their dead in the underground chamber. Remains of fifteen individuals were found in the location.
Homo naledi
Fossils of a Homo naledi are pictured during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Homo naledi
Fossils of a newly discovered ancient species Homo naledi are displayed during their unveiling outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Homo naledi
Hand bones are among the skeleton pieces of a Homo Naledi displayed in Maropeng, outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Scientists believe Homo naledi walked upright.
Homo naledi
Fossils of a newly discovered Homo naledi on display near Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.
Homo naledi
Skeletal remains of Homo naledi are pictured outside Johannesburg, September 10, 2015.